Asset Performance Management | More Than Just EAM
EAM/CMMS is a tool. APM is the operating system—linking strategy, data standards, work management, analytics, and people so assets perform safely and predictably. This article lays out the APM building blocks and how to use them together—not just at go-live, but every day.
Schedule your APM Optimizer Suite Demo
What APM is (and Isn't)
Gartner defines Asset Performance Management (APM) as encompassing the capabilities of data capture and cleansing, integration, visualization, and analytics/digitalization tied together for the explicit purpose of improving the reliability and availability of physical assets. To maximize the equipment's return on investment (ROI) and reduce risk factors, APM includes the following concepts:
- Risk Management/Mitigation
- Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA)
- Condition Monitoring
- Predictive Forecasting
- Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Together the process will determine the inherent reliability and performance of an asset in its operational context and serves to:
- Increase the level of performance to the inherent level by the application of preventive and predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, machine learning, etc.
- Increase the inherent performance level, using data collection and problem-solving, through the introduction of optimized strategies, modifications to the machine design, and the operating conditions or methods
The Four Quadrants of APM:
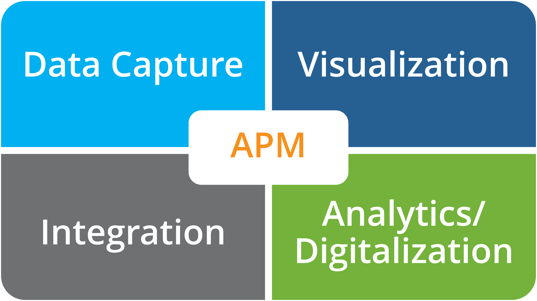
DATA CAPTURE: Starts with the development of a "Data Management Process Standard" to include master data, transactional data, process data (SCADA), monitoring data (CBM/OIL/Vibration/Ultrasonic/etc.), and validation of data and data sources.
INTEGRATION: Capability to integrate with existing operational, safety, and maintenance systems as well as other 3rd party systems to create a digitalized environment.
VISUALIZATION: Capability to display asset health information from the data collected into a dashboard format that can be configurable to end-users' needs. Transforming data to information and then to visualization.
ANALYTICS/DIGITALIZATION: Capability to perform insights into equipment health and predictive alerts to help quickly address pending issues before they impact customer experience. Potentially plotting the performance on a P-F curve and calculating the potential beginning of the failure.
APM vs EAM vs CMMS
ASSET PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT (APM)
APM is designed for the decision-making of safe, reliable, and efficient operation of equipment and infrastructure leading to operational and maintenance excellence. APM platforms track and manage the performance of operational assets to increase availability and reduce risks.
ENTERPRISE ASSET MANAGEMENT (EAM)
EAM is designed for maintenance execution with financial and resource tracking. EAM is computer software that handles every aspect of running an asset-intensive organization. EAM applications include features such as asset lifecycle management, preventive maintenance scheduling, warranty management, integrated mobile wireless handheld options, and portal-based software interfaces.
COMPUTERIZED MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (CMMS)
CMMS is designed to automate and streamline all tasks relating to maintenance management. CMMS solutions manage maintenance to ultimately extend physical asset lifespan and are primarily used by maintenance personnel.
A Very Important Realization
The realization that all systems are distinctly different yet need to be integrated is very important. The purchase and use of an EAM alone will leave a large void in an APM infrastructure.
To our knowledge, no EAM has suitable data relationships to fulfill the requirements of all four APM quadrants. To be effective within an Asset Management program, an organization needs systems, software, as well as work processes, and standards to ensure all quadrants have the required capabilities to achieve desired outcomes.
Creating a Sustainable APM Program
All organizations have some system of maintenance management with most having an EAM or CMMS. In addition, most organizations track equipment performance and try to eliminate chronic or high-consequence failures. Where we find the problem mostly occurs, is that most companies do not apply these processes very efficiently or effectively. Here's why:
Data Quality
EAM data isn't often set up properly and as a consequence, the use of poor data quality impacts the results. This consequence is often self-perpetuating because if the Maintenance Management System (MMS) is not configured correctly or used properly it will not contain valid and useful information. If it does not contain valid and useful data, fewer people will use it leading further to its demise.Reactive Maintenance Culture
Many maintenance departments are more reactive than they need to be. When reactive maintenance prevails, their MMS and other maintenance systems tend to be forgotten and data entry is not completed timely or at all.Reliability Strategy
The Reliability Strategy was not developed properly in the first instance and a Strategy Development and Review System is completely missing. In the past, project managers and financiers have often failed to take a lifecycle view of operating and maintenance costs. While this situation is changing, for most plants in the current operation, the reliability strategy has never been properly developed and/or comprehensively reviewed. This is potentially due to data being unavailable or the failure modes were not understood or documented. In recent years, the techniques available to develop strategies have been considered too resource-intensive to be used as review tools (RCM being the case in point). As a result, more organizations are turning to a PM Optimization (PMO) strategy using APM OptimizerTM to deliver results one-sixth of the time.Downtime Data Management
Traditionally, downtime data management has not been set up strategically and does not collect the right data or is not gathering data points to the correct asset. In most companies, data or information visualization systems appear to be using more of a shotgun approach rather than targeting specific data, leading to misinformed decision-making. This is most often because a data collection program has not been based on a defined reliability improvement strategy originating out of an RCM or Strategy Optimization study. Within the APM Optimizer Suite of tools, all data points are aligned to an acceptable limit defined in the development of the reliability strategy and against a specific asset within the asset hierarchy.Investigation Management
In some organizations, incident reporting and investigation management are fragmented and overly cumbersome. Each investigation takes too long to administer because the information and data that should be easily obtained from other systems, EAM or other data collection systems, is either missing or difficult to obtain, and the processes and status of work lack visibility. Typically, such systems have evolved without any structured process or means to track, manage, and archive these investigations. With APM Optimizer, there is a single integrated application system where all APM information can become part of an organization's EAM program.An APM program should consist of five primary elements or domains that are all-inclusive of a World-Class APM solution. The five APM domains are Leadership, Data Management, Strategy Management, Work Management, and Investigation Management.

In addition to these domains, APM programs should follow a structured disciplined approach. The approach should be developed using an APM Sustainability Engagement Framework consisting of 5 key steps: Assess/Analysis, Develop/Design, Quick Wins, Long-Term Impact. and Sustainability. With the five APM domains and a structured disciplined approach, your APM initiative will be set for success.
Success in Your Plant is Only a Few Months Away
Nexus Global specializes in APM. With proper implementation, our APM Optimizer Suite and overall APM program can cut maintenance-related downtime by 50% in almost all situations.
With a proactive mindset as well as leadership sponsorship and commitment, APM can be implemented site-wide in as little as 12 months. Implementation is usually completed area by area or based on a corporate strategy across sites. With a structured and sponsored APM program, results start coming through to the bottom line as soon as the implementation is commenced. Below are some common results from an APM program:

Are you ready to make your operation safer and more reliable while helping to ensure optimal performance at a lower sustainable cost? Contact us to learn more about our APM solutions success stories or request a demo to see our APM software in action.
FAQ
How is APM different from EAM?
EAM/CMMS is the system of record for work and assets; APM is the operating system that connects strategy, work, data, and investigation to deliver outcomes.
Do we need new software to start APM?
Not necessarily—begin with standards and routines; then use APM tools to template strategies and improve utilization.
What’s the first practical step?
Run an APM maturity review, pick quick wins in work and data standards, and stand up governance.
What KPI improvements should we see first?
Planning lead time, schedule adherence, clean closeout compliance (time/parts/failure/cause), and clearer MTBF/MTTR trending.
Who owns APM?
A cross‑functional team: operations, maintenance, reliability/engineering, and IT/OT—sponsored by asset leadership; planners/supervisors own day‑to‑day cadence.
How do APM pillars map to our org?
Strategy → reliability/engineering; Work → planning/scheduling & supervisors; Data → master data/CMMS admins; Investigation → RCA/quality/HSE.
How long does an APM roadmap take to stand up?
Typical cadence: assessment in 2–4 weeks, 30/60/90‑day quick wins, and quarterly governance thereafter.
What governance is required?
Named data owners/stewards, change control for strategies and code sets, monthly audits, and a visible approvals/change log.
How does APM interact with analytics/IIoT?
APM defines the questions and data standards—so sensor/analytic outputs map cleanly to assets, codes, and strategies inside EAM/CMMS.
Common pitfalls to avoid?
Over‑customizing the CMMS, skipping data standards, weak job plans, no closeout discipline, and treating APM as a one‑time project.
What quick wins usually pay back fast?
Publish hierarchy + class/attribute model, standardize top 20 job plans, enforce closeout fields, and start weekly schedule reviews.
How do we sustain APM?
Leader standard work (reviews/scorecards), quarterly strategy and code‑set reviews, continuous training, and automated data quality checks.
Does APM work outside utilities?
Yes—APM is industry‑agnostic and applies across power, mining, manufacturing, terminals, life sciences, and more.
Where does change management fit?
Throughout: communicate the why, role‑based training, job aids, and coaching at the point of use to embed new routines.
Topics: Data Management, Work Management, Article, Investigation Management, Leadership, Strategy Management

Posted by
Larry Olson | CMRP, CRL, CAMA
CEO, Nexus Global | Larry is one of the leading global Shutdown/Turnaround, Asset Integrity, and Maintenance strategists. With over 30+ years of business & maintenance experience, he has carried out a variety of roles from Project Manager, Change Management Specialist to Director of Reliability & Integrity Assurance Excellence.




